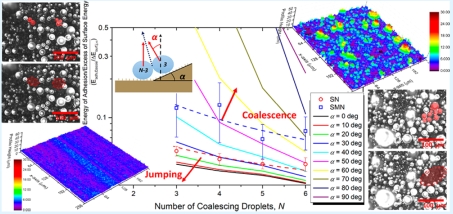
Fundamental Physics of Condensation Phase-Change
Interactions between liquids and solid surfaces are relevant for many industrial, biological and pharmaceutical applications. Wettability, roughness, chemical heterogeneities, temperature and pressure play an important role during phase change. Understanding the effect of these parameters during evaporation and condensation at the macro- and at the micro-scale is paramount for the design of more efficient heat transfer processes and novel energy systems.
 Orejon et al., RSC Advances 6 (43) 2016
Orejon et al., RSC Advances 6 (43) 2016
Zhang et al., ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2017
Energy Storage via Phase Change Materials (PCMs)
Phase Change Materials (PCMs) have received special attention in the last decade due to the ability to store thermal energy via latent heat of fusion/solidification. However these materials lack on high thermal conductivity, which limits the energy storage. This latter can be enhanced by small addition of micro- or nano- scaled particles. The great variety, geometry and size of particles represents a wide area of study with great potential for the control and enhancement of the PCMs thermal conductivity and for the further understanding of nano-scale thermal transport.
 Harish et al., Applied Thermal Engineering 80 2016
Harish et al., Applied Thermal Engineering 80 2016
Storage of Hydrogen Chemical Energy
Sponge iron reaction (SIR) process has been proposed for the store the hydrogen chemical energy via Redox (Oxidation and Reduction) reactions. The storage capacity of these sponges is limited, but they offer the possibility of storing energy from renewable sources that otherwise would be wasted. The study and characterization in depth of different metals and alloys, synthesis processes, energy systems design and Redox Cycles is vital.
Stabilization/Solidification of Metallurgic Residual Waste
Waste products from metallurgic industry, EAFD (electric arc furnace dust) and slag cannot be disposed in a landfill due to the amount of heavy metals present in this dust. Stabilization and Solidification of EAFD, slug and fly ashes using geopolymerization technique has yielded promising results meeting lixiviation and compressive strength criteria. The use of KOH (potassium hydroxide) during our fabrication process yielded compressive strengths up to 5 times greater mechanical resistance.
Electrowetting of Pure Fluid and Nanofluid Droplets
The importance of manipulating fluids without mechanical parts has gained recent interest. An applied voltage to a droplet modifies the interfacial tension liquid-gas, setting droplet in motion if the applied voltage is enough. Furthermore, the fine control of the contact line motion by a voltage applied has the ability to enhance internal droplet mixing or control the final deposits. Enhancement in electrowettability of nanofluids when compared to base fluid has been reported.
 Orejon et al. JCIS 407, 2013 & Orejon et al. APL 102 (20) 2013
Orejon et al. JCIS 407, 2013 & Orejon et al. APL 102 (20) 2013